Key Takeaway: Atlassian bets on AI-powered browsers with massive acquisition of The Browser Company, targeting workplace productivity revolution.
Software Giant Makes Bold Move into Browser Market
Atlassian Corporation announced Thursday it will acquire The Browser Company for $610 million in cash, marking the enterprise software maker’s largest bet on artificial intelligence and workplace productivity tools. The deal brings together Atlassian’s collaboration platform expertise with The Browser Company’s innovative Arc and Dia browsers, targeting the growing market for AI-powered workplace solutions.
The acquisition positions Atlassian to challenge traditional web browsers by creating tools specifically designed for modern knowledge workers. “Today’s browsers weren’t built for work; they were built for browsing,” said Atlassian CEO Mike Cannon-Brookes in announcing the deal.
Strategic Rationale Behind the $610M Deal
Targeting Enterprise Browser Gap
The acquisition addresses a fundamental problem in workplace productivity: while 85% of enterprise workflows occur within web browsers, current browsers lack the contextual awareness needed for complex work tasks. Traditional browsers treat every tab equally, without understanding work priorities or connecting different applications seamlessly.
Atlassian identified this gap as a strategic opportunity to extend its collaboration tools directly into the browser environment. With over 300,000 customers including 80% of Fortune 500 companies, Atlassian can provide The Browser Company immediate access to a massive enterprise user base.
AI-First Approach to Web Browsing
The Browser Company’s latest innovation, Dia, represents a breakthrough in AI-powered browsing technology. Launched in beta this June, Dia integrates artificial intelligence directly into core browser functions, enabling features like automatic page summarization, multi-tab question answering, and intelligent task automation.
Example of the Dia AI browser interface helping a user find a cheaper alternative beach towel within the shopping experience.
This AI-first approach aligns with Atlassian’s vision of creating intelligent workplace tools that anticipate user needs rather than simply facilitating basic web access.
The Browser Company’s Innovation Portfolio
Arc Browser: Reimagining Web Navigation
Founded in 2019 by CEO Josh Miller, The Browser Company first gained attention with Arc, a browser that fundamentally reimagines tab and workspace management. Arc organizes tabs into customizable “spaces” and offers features like built-in whiteboards, automatic tab archiving, and personalized interfaces. Arc browser interface by The Browser Company showing a webpage with navigation tabs and site content.
Despite building a dedicated following among tech enthusiasts and raising $128 million from prominent investors including LinkedIn’s Jeff Weiner and Figma’s Dylan Field, Arc never achieved mainstream adoption.
Dia: The Next-Generation AI Browser
The company’s pivot to Dia represents a more ambitious vision for AI-integrated browsing. The browser can assist with complex tasks like writing, planning, learning, and shopping while maintaining contextual understanding across multiple tabs and applications.
Market Context and Competitive Landscape
Browser Wars Intensify with AI Focus
The acquisition comes as the browser market experiences its most significant disruption in years. While Google Chrome maintains approximately 69% global market share, the emergence of AI-first browsers is creating new competitive dynamics.
Companies like OpenAI and Perplexity are developing their own AI-powered browsers, while Perplexity recently made an unsolicited $34.5 billion bid for Google’s Chrome browser. This competition reflects the strategic importance of browsers as the primary interface for AI-driven work experiences.
Atlassian’s Acquisition Strategy
Building Through Strategic Purchases
The Browser Company acquisition continues Atlassian’s expansion strategy through targeted startup acquisitions. Since 2010, the company has completed numerous strategic purchases, including Trello for $425 million in 2017 and Loom for $975 million in 2023.
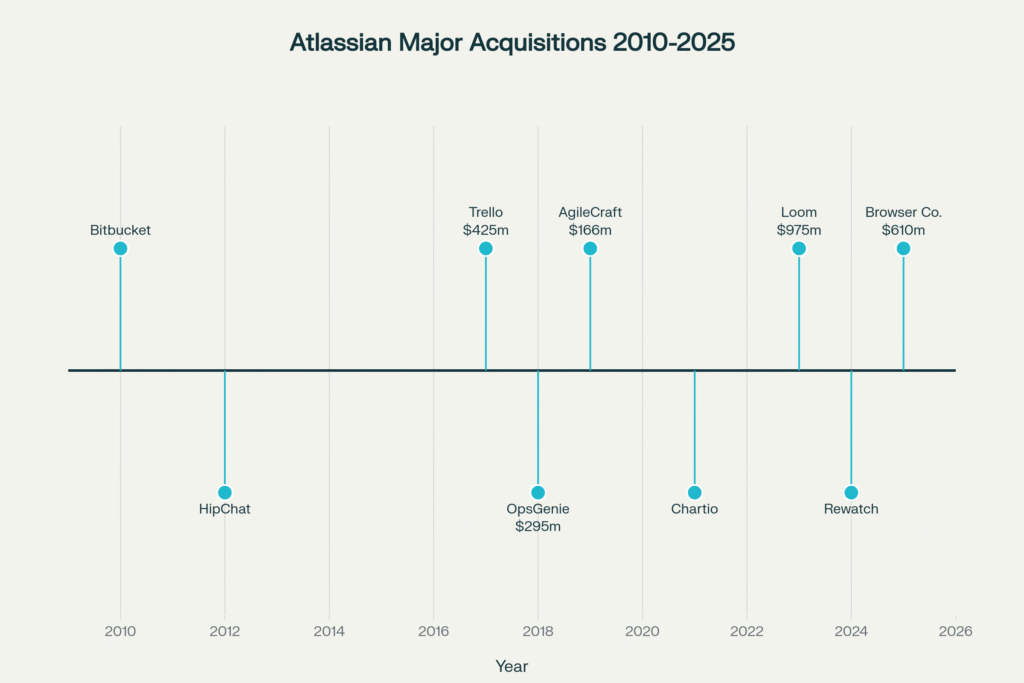
Each acquisition has strengthened Atlassian’s position in workplace collaboration, with the Loom integration proving particularly successful in adding asynchronous video messaging capabilities.
Integration Plans and Timeline
Independent Operations with Shared Vision
The Browser Company will operate independently under Atlassian while continuing Dia’s development. The combined teams plan to create a browser optimized for Software-as-a-Service applications commonly used by knowledge workers.
Josh Miller confirmed the deal will enable faster hiring, accelerated feature development, and expansion across multiple platforms. The acquisition is expected to close in Atlassian’s fiscal second quarter of 2026, subject to standard regulatory approvals.
Financial Details and Market Impact
Premium Valuation Reflects AI Potential
The $610 million all-cash transaction represents a premium over The Browser Company’s most recent $550 million valuation from its 2024 funding round. Atlassian will fund the purchase through existing cash reserves, leveraging its strong financial position with over $4.4 billion in annual revenue.
Industry Implications
Challenging Google’s Browser Dominance
Industry analysts view the acquisition as a strategic bet on AI-driven interfaces becoming the future of workplace productivity. If successful, the integration could provide enterprises with viable alternatives to Google Chrome while reducing dependence on Google’s ecosystem.
The deal also highlights how established enterprise software companies are acquiring innovative startups to remain competitive in the AI revolution. For users, the combination promises more intelligent, context-aware tools that understand workplace needs rather than simply facilitating web browsing.
Future of Work-Optimized Browsing
The success of this acquisition could establish precedents for how legacy technology firms navigate AI transformation through strategic startup acquisitions. The combined platform aims to create “personal work memory” that seamlessly connects applications, tabs, and tasks across different work contexts.
Source: Reuters, WebProNews, and additional industry reporting